2D materials-based Heat Waste Recovery of LED (HeatRecovery)
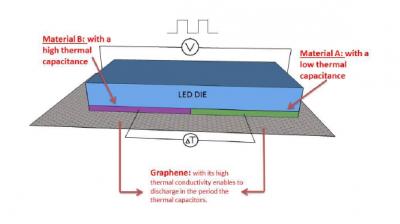
Most of the electricity in an LED becomes heat rather than light (about 70% heat and 30% light). The thermal energy dissipated by the LED is intended to be transformed into electrical energy to be reused as useful signal for the LED itself, and to increase the efficiency of the SSL system. The idea is to reuse the thermal energy dissipated by the LED, which is accumulated by the thermal capacitance of the materials (Cth=dQ/dT), which expresses the amount of energy to be stored in a certain material to increase its temperature by one degree. Layer stack is between LED and heatsink, two materials with different values of thermal capacitance are placed in contact with the substrate. During the on phase of the LED, due to the different thermal capacitance, the temperature in the two materials increases with different slope. This creates a temperature gradient during each half cycle of the signal. This temperature signal is intended to be transformed into electrical energy to be reused as useful signal for the LED itself, and to increase the efficiency of the SSL system.
Project data
| Researchers: | Yelena Grachova, GuoQi Zhang |
|---|---|
| Starting date: | September 2014 |
| Closing date: | September 2018 |
| Sponsor: | Philips |
| Contact: | GuoQi Zhang |